Exporting Kubernetes Events to AWS Elastic Search

Kubernetes Events are not persisted by default. Using a log aggregator like AWS Elastic Search will allow us to persist these events and use it to do forensics later. Later on you can also use event-exporter to alert on these events using prometheus.
Kubernetes Event Exporter
Events are a type of logs in cluster that helps us debug or troubleshoot. Events are available when we run kubectl describe pods or kubectl get events
The problem is that by default they only last for 1 hour in order to conserve etcd. In EKS they are only available for 5 minutes by default.
In theory you can get all kubernetes events by running kubectl get events --watch and pumping the results of that into a sink like elasticsearch. However we want to be able to filter only the events we need.
To export these `events` we will be using OpsGenie's kubernetes-events-exportertool.
Optional Prerequisites
- Running Kubernetes Cluster
- Running Elastic Search Cluster
For the purposes of demo we will be using AWS Full managed Services but you can use any flavor of Kubernetes or Elastic Search:
- Kubernetes: AWS EKS
- Elastic Search: AWS Elastic Search
(Optional) Setting up AWS ElasticSearch
Please skip this part if you have a running Elastic Search Cluster already. If you follow this part please be aware that this is for testing purposes only in production ensure that your Elastic Search Cluster is production ready.
For testing purposes we will manually create an elastic search cluster with username password. First make sure that your AWS CLI is on the latest version
pip3 instlal awscli --ugpradeget the id of aws managed KMS key called aws/es
ES_KMS_ID=$(aws kms list-aliases | jq -r '.Aliases[] | select(.AliasName=="alias/aws/es").TargetKeyId')export environment variables needed to setup AWS ElasticSearch
USERNAME=fakeuser
PASSWORD=Fakepassword1!
ES_DOMAIN=kubernetes-events-2
AWS_ACCOUNT=00000000000Create the AWS Elastic Search via AWS CLI
aws es create-elasticsearch-domain \
--region eu-west-1 \
--domain-name $ES_DOMAIN \
--domain-endpoint-options EnforceHTTPS=true,TLSSecurityPolicy=Policy-Min-TLS-1-2-2019-07 \
--elasticsearch-version 7.4 \
--elasticsearch-cluster-config InstanceType=r4.large.elasticsearch,InstanceCount=1 \
--ebs-options EBSEnabled=true,VolumeType=standard,VolumeSize=10 \
--node-to-node-encryption-options Enabled=true \
--encryption-at-rest Enabled=true,KmsKeyId=$ES_KMS_ID \
--advanced-security-options "{\"Enabled\":true,\"InternalUserDatabaseEnabled\":true,\"MasterUserOptions\": {\"MasterUserName\":\"$USERNAME\",\"MasterUserPassword\":\"$PASSWORD\"}}" \
--access-policies "{\"Version\": \"2012-10-17\", \"Statement\": [ { \"Effect\": \"Allow\", \"Principal\": {\"AWS\": \"*\" }, \"Action\":\"es:*\", \"Resource\": \"arn:aws:es:us-west-1:$AWS_ACCOUNT:domain/$ES_DOMAIN/*\" } ] }"Testing AWS Elastic Search Setup
ES_ENDPOINT="https://search-kubernetes-events-fake-endpoints-123.eu-west-1.es.amazonaws.com"
AUTH=$(echo -ne fakeuser:Fakepassword1! | base64)
echo $AUTH
curl -XGET "$ES_ENDPOINT" -H "Authorization: Basic $AUTH"
curl -XPUT "$ES_ENDPOINT/movies/_doc/1?pretty" -H "Authorization: Basic $AUTH" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '{ "title": "John Carter" }'
curl -XGET "$ES_ENDPOINT/movies/_doc/1?pretty" -H "Authorization: Basic $AUTH"For more ES Queries:
- https://sysadmins.co.za/getting-started-with-aws-elasticsearch-service/
(Optional) Setting up Kubernetes using AWS EKS
brew tap weaveworks/tap
brew install weaveworks/tap/eksctl
git clone git@github.com:kenichi-shibata/cluster-test
cd eksctl/
eksctl create cluster -f dev-cluster-1.yaml
# wait for the cluster to be createdSetting up events-exporter
Make sure to change the elasticsearch.hosts[] in the configmap.yaml file to the actual Elastic Search Endpoint. Or if you have a different authentication make sure you specify that instead.
Create three yaml files in order
roles.yamlconfigmap.yamldeployment.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: monitoring
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
namespace: monitoring
name: event-exporter
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: event-exporter
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: view
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
namespace: monitoring
name: event-exporterapiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: event-exporter-cfg
namespace: monitoring
data:
config.yaml: |
route:
# Main route
routes:
# This route allows dumping all events because it has no fields to match and no drop rules.
- match:
- receiver: elasticsearch-dump
receivers:
- name: "elasticsearch-dump"
elasticsearch:
hosts:
- https://search-replace-this-endpoint-.eu-west-1.es.amazonaws.com
index: kube-events
indexFormat: "kube-events-{2006-01-02}"
username: fakeuser
password: Fakepassword1!apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: event-exporter
namespace: monitoring
spec:
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: event-exporter
version: v1
spec:
serviceAccountName: event-exporter
containers:
- name: event-exporter
image: opsgenie/kubernetes-event-exporter:0.7
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
args:
- -conf=/data/config.yaml
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /data
name: cfg
volumes:
- name: cfg
configMap:
name: event-exporter-cfg
selector:
matchLabels:
app: event-exporter
version: v1Check logs if authenticaiton worked
kubectl logs deployment/event-exporter -n monitoring
Create a failed event
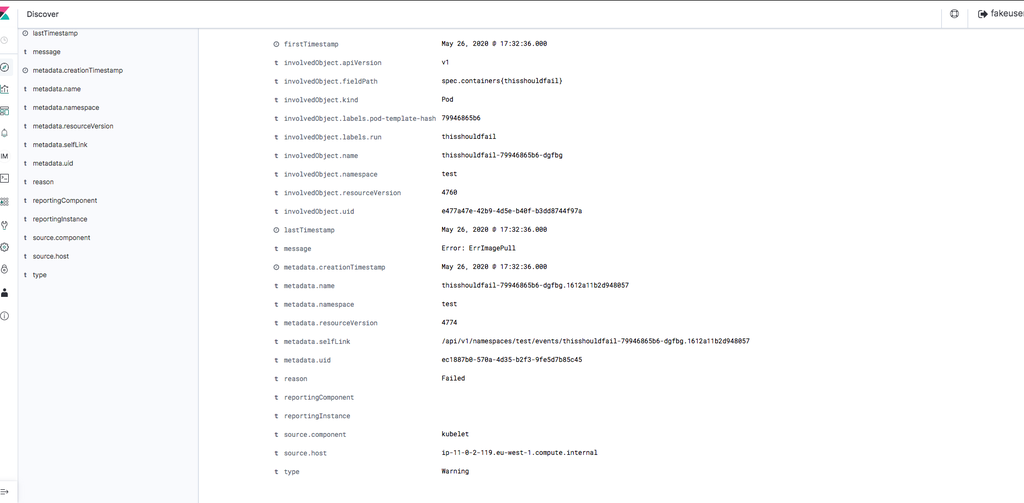
kubectl run -it --image=fakeimage/fakeimage123:123 thisshouldfail -n test
If you want to make the kubernetes fields searchable in elasticsearch you might need to index them like kube-events-*
If you want search try to reindex them management -> index pattern -> new index pattern --> kube-events-* --> refresh icon
If all went well you should see something like this entries
Elastic Search Indexing
Get similar stories in your inbox weekly, for free
Share this story:

Kenichi Shibata, Cloud Solution Architect @ shibata.co.uk
Cloud Solution Architect
Latest stories
How ManageEngine Applications Manager Can Help Overcome Challenges In Kubernetes Monitoring
We tested ManageEngine Applications Manager to monitor different Kubernetes clusters. This post shares our review …
AIOps with Site24x7: Maximizing Efficiency at an Affordable Cost
In this post we'll dive deep into integrating AIOps in your business suing Site24x7 to …
A Review of Zoho ManageEngine
Zoho Corp., formerly known as AdventNet Inc., has established itself as a major player in …
Should I learn Java in 2023? A Practical Guide
Java is one of the most widely used programming languages in the world. It has …
The fastest way to ramp up on DevOps
You probably have been thinking of moving to DevOps or learning DevOps as a beginner. …
Why You Need a Blockchain Node Provider
In this article, we briefly cover the concept of blockchain nodes provider and explain why …
Top 5 Virtual desktop Provides in 2022
Here are the top 5 virtual desktop providers who offer a range of benefits such …
Why Your Business Should Connect Directly To Your Cloud
Today, companies make the most use of cloud technology regardless of their size and sector. …
7 Must-Watch DevSecOps Videos
Security is a crucial part of application development and DevSecOps makes it easy and continuous.The …